How to Integrate an Efficient Backup into your Workflow
High scale enterprises with a large number of employees have their own regular backup routines that are obligatory to maintain. Especially these firms face a high risk of losing valuable data; we are all familiar how prone computers are to crashes and that they have to be well protected against viruses.
While the importance of the backup process increases in larger scale companies, many small companies and freelancers who run a small business don’t allocate the backup process at the same level of importance in their company routine. This should be well thought out and can prevent unforeseen loss of data and by all means keep the business running smoothly.
[fblike]
Although a small business has less hardware and workflow compared to a large company, they still face the same risks. You will find numerous people who have lost a large amount of work, sometimes even whole projects, due to a virus that had attacked their computer or have experienced an unfortunate system crash. Such a disaster can affect one's time, project files and costs which are the main important factors in any project. It’s worth the time and effort to plan a backup process, add it to your daily tasks and schedule a time to backup your work on a regular basis.
In this post, we will discuss the backup process and how to apply it to small firms as well as freelance businesses; the different types of backups you can do and exactly which devices to use for your backup process. Tools and softwares you can also use will be introduced. First, let us start by understanding the backup process and its different types.
 It is a multi-threaded application that you can use to backup files and folders from the local machine and store them in another destination or upload it to an FTP account. Cobian backup can save the stored files in both a compressed and non-compressed format.
It is a multi-threaded application that you can use to backup files and folders from the local machine and store them in another destination or upload it to an FTP account. Cobian backup can save the stored files in both a compressed and non-compressed format.
 DeltaCopy is an open source backup tool that is based on the incremental backup method to save the files. It reduces the backup and restores time. DeltaCopy can run based on a scheduled time with one click to restore the saved files.
DeltaCopy is an open source backup tool that is based on the incremental backup method to save the files. It reduces the backup and restores time. DeltaCopy can run based on a scheduled time with one click to restore the saved files.
 With Acebackup, you can store the backed up files on different storage media as well as the ability to upload the backup files to a remote FTP account. Also, it supports different compression and encryption methods for the files. Similar to other backup tools, it can be scheduled to do the backup process in specified times.
With Acebackup, you can store the backed up files on different storage media as well as the ability to upload the backup files to a remote FTP account. Also, it supports different compression and encryption methods for the files. Similar to other backup tools, it can be scheduled to do the backup process in specified times.
 SyncToy is basically a synchronization application between files and folders and it can create backup copies of these files and folders. SyncToy's new version includes better error handling than the previous one. In addition to the new features, it also includes the ability to filter files based on one or more attributes and manage folders through the command line interface.
SyncToy is basically a synchronization application between files and folders and it can create backup copies of these files and folders. SyncToy's new version includes better error handling than the previous one. In addition to the new features, it also includes the ability to filter files based on one or more attributes and manage folders through the command line interface.
 Personal-backup saves the backup files to both local and remote storage locations with the ability to include or exclude folders and files based on manual selection or using filters. It maintains the original files architecture and compresses the files as Gzip or Zip.
Personal-backup saves the backup files to both local and remote storage locations with the ability to include or exclude folders and files based on manual selection or using filters. It maintains the original files architecture and compresses the files as Gzip or Zip.
 Allway Sync is a free, personal backup tool that allows you to backup files and folders as well as synchronizes them with an easy to use interface. It can also backup files on local devices or through the network.
Allway Sync is a free, personal backup tool that allows you to backup files and folders as well as synchronizes them with an easy to use interface. It can also backup files on local devices or through the network.
 Hinxsoft backup tool allows automatic backup of files and folders with multi-language support. This application is written in Java and comes with a simple interface. The backed up files can be saved on local devices or FTP using SSL and SFTP.
Hinxsoft backup tool allows automatic backup of files and folders with multi-language support. This application is written in Java and comes with a simple interface. The backed up files can be saved on local devices or FTP using SSL and SFTP.
 Comodo is a free backup and recovery application that includes some useful features in addition to the ordinary backup features such as quickly restoring data, multiple compression options, email notification with the backup status and securing features through password and data encryption.
Comodo is a free backup and recovery application that includes some useful features in addition to the ordinary backup features such as quickly restoring data, multiple compression options, email notification with the backup status and securing features through password and data encryption.
 SyncBackupSE saves files with ‘fast backup’ and ‘smart synchronization’. It keeps the previous backup versions and creates a new version with every new backup.
SyncBackupSE saves files with ‘fast backup’ and ‘smart synchronization’. It keeps the previous backup versions and creates a new version with every new backup.
 Acronis is another commercial backup tool; it lets you schedule the backup process and create encrypted backup content. It also provides a secure backup for files and gives you the ability to adjust your system resources such as the CPU and bandwidth allocated to the Acronis backup process. Acronis allows you to recover files from different points in the backup version as well, so you can revert to the points where the data isn’t corrupted, and it provides protection to multiple computers at the same time.
Acronis is another commercial backup tool; it lets you schedule the backup process and create encrypted backup content. It also provides a secure backup for files and gives you the ability to adjust your system resources such as the CPU and bandwidth allocated to the Acronis backup process. Acronis allows you to recover files from different points in the backup version as well, so you can revert to the points where the data isn’t corrupted, and it provides protection to multiple computers at the same time.
 ChronoSync is a Mac backup application that provides a tool to synchronize files, backup files and create bootable backups where you can boot to your backup files and run your Mac from the backup. Similar to the rest of the backup tools, ChronoSync provides a scheduled sync of your files.
ChronoSync is a Mac backup application that provides a tool to synchronize files, backup files and create bootable backups where you can boot to your backup files and run your Mac from the backup. Similar to the rest of the backup tools, ChronoSync provides a scheduled sync of your files.
 It is an easy to use backup utility for your Mac files and folders as it provides the ability to create a bootable copy of the hard disk, compression and encryption for the files, automatic upgrades and the ability to work in the background while your applications are running.
It is an easy to use backup utility for your Mac files and folders as it provides the ability to create a bootable copy of the hard disk, compression and encryption for the files, automatic upgrades and the ability to work in the background while your applications are running.
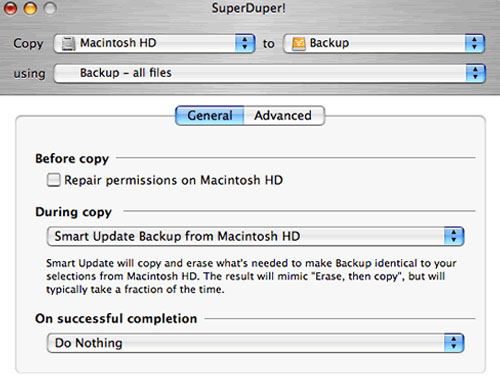 This utility includes common backup tasks along with simple and clear language. Also, it is working perfect with both Intel and Power PC Macs.
This utility includes common backup tasks along with simple and clear language. Also, it is working perfect with both Intel and Power PC Macs.
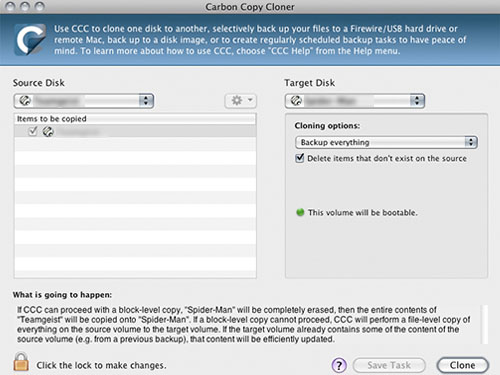 It is a free backup application that lets you backup, synchronize and clone your data using the incremental backup to create fast backups since it only saves the changes that happened based on the previous version of the backup data. Carbon Copy archives the items that have been deleted from the source and backs up the files to the hard drive or a disk image.
It is a free backup application that lets you backup, synchronize and clone your data using the incremental backup to create fast backups since it only saves the changes that happened based on the previous version of the backup data. Carbon Copy archives the items that have been deleted from the source and backs up the files to the hard drive or a disk image.
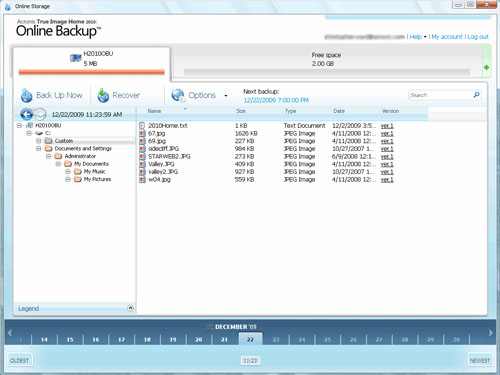 Acronis provides an online backup tool that lets you backup data up to 250GB with full security and protection. Also you can use it to store your data and download it from anywhere without the need to transport your data everywhere you go. Acronis Online Backup subscription can be either on a monthly or a yearly plan. You can use the account to backup one or more PCs or laptops.
Acronis provides an online backup tool that lets you backup data up to 250GB with full security and protection. Also you can use it to store your data and download it from anywhere without the need to transport your data everywhere you go. Acronis Online Backup subscription can be either on a monthly or a yearly plan. You can use the account to backup one or more PCs or laptops.
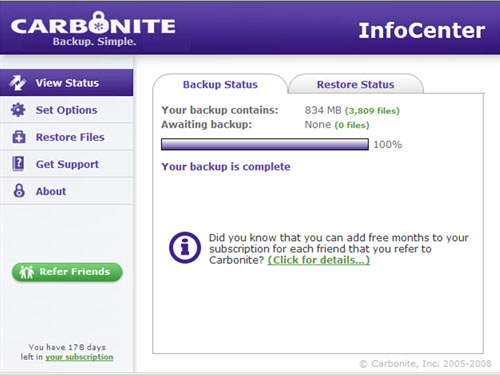 Carbonite provides different subscription plans to join their backup service which include one, two or three year periods. Carbonite provides secure online storage for the backup by using up-to-date encryption.
Carbonite provides different subscription plans to join their backup service which include one, two or three year periods. Carbonite provides secure online storage for the backup by using up-to-date encryption.
 Mozy is one of the most comprehensive online backup utilities that provides encryption for the backed up data as well as automatic detection of changes in the files and backing up. On the other hand, it supports the backup of open and locked files and an automatic, scheduled backup. Mozy is using the incremental backup method to store the files and lets you decide the bandwidth you would like to dedicate for the backup process. Mozy provides a free account that includes 2 GB of free backup space to trial without the need to add any payment information.
Mozy is one of the most comprehensive online backup utilities that provides encryption for the backed up data as well as automatic detection of changes in the files and backing up. On the other hand, it supports the backup of open and locked files and an automatic, scheduled backup. Mozy is using the incremental backup method to store the files and lets you decide the bandwidth you would like to dedicate for the backup process. Mozy provides a free account that includes 2 GB of free backup space to trial without the need to add any payment information.
 This utility is using the incremental method and saves only the changes that occur in the files; this saves a lot of space and increases the backup speed and can be helpful in the online backup process. IDrive provides other features such as the option to automate the backup of common files such as photos, documents and videos. IDrive can detect changes in files and back it up every 10 minutes as well as apply encryption to it. Also, it can backup open and locked files, external hard drives and restore data from anywhere using the fast search feature. You can try IDrive through the free account which provides 2 GB free storage to store files and backup data.
This utility is using the incremental method and saves only the changes that occur in the files; this saves a lot of space and increases the backup speed and can be helpful in the online backup process. IDrive provides other features such as the option to automate the backup of common files such as photos, documents and videos. IDrive can detect changes in files and back it up every 10 minutes as well as apply encryption to it. Also, it can backup open and locked files, external hard drives and restore data from anywhere using the fast search feature. You can try IDrive through the free account which provides 2 GB free storage to store files and backup data.
 Dropbox includes file sync, file sharing and online backup for your files. It enables automatic updates for the files, even if you are working offline, as once you connect your computer to the internet, Dropbox starts to synchronize the files and makes sure you have the latest updates on the server. Through the paid account, you can undo file changes to an unlimited number of versions. You can try Dropbox through their free account with 2 GB of space and undo for up to 30 days.
Dropbox includes file sync, file sharing and online backup for your files. It enables automatic updates for the files, even if you are working offline, as once you connect your computer to the internet, Dropbox starts to synchronize the files and makes sure you have the latest updates on the server. Through the paid account, you can undo file changes to an unlimited number of versions. You can try Dropbox through their free account with 2 GB of space and undo for up to 30 days.
Backup methods
The backup refers to the process where a copy of the data is taken and saved to be retrieved in case the original data is lost or damaged. The risk of data loss occurring is around 66% — a statistic found on Wikipedia. There are many backup methods as we will see below; these types are based on how each method interacts with the content, updates and information. Most backup tools and software provide the option to create one or more of the following types:Full backup
This is the standard concept of a backup process and the starting stage for other backup methods. Full backups take a copy of all the files, including both the data and the overall structure. The full backup isn’t performed frequently; usually after major changes in the system, such as changing the operating system or a large number of files being modified. It is also done as the starting point for any other backup method. The advantage of this method is that it’s the simplest. The disadvantage is that the backup file is very large and it also takes the longest time to restore the data.Differential backup
In most cases, the changes only affect small amounts of data or specific folders; the full backup wouldn’t be necessary in this case. The differential backup is the next method to backup files and it requires a full backup at the beginning. In this method, you take a backup of the files that are changed in comparison to the base full backup. For example, if you make a full backup of your system on day one, the differential backup on day two only saves the files that have changed since day one. On day three, the differential backup saves the changes that have occurred since the first full backup on day one. The advantage of this method is that it takes less time to restore the saved backup. The disadvantage of this is that the frequent backing up using this method produces files that can be larger than the full backup file itself.Incremental backup
This method is similar to the differential backup. The only difference is that this type saves the changes from the last backup whether it is full, differential or another incremental backup. The advantage of this process is that it takes less time to complete as it only saves the changes from the last backup. The disadvantage of this backup type is that it takes a long time to restore the data because each previous backup must be processed before completing the restore action. Although all the backup applications depend on the full backup as the initial backup process, these tools may implement two or more backup methods. Each of the above methods varies in the final size of the backup. It is important to determine the backup output or the device you will choose for the backup as we will see later in choosing the backup devices.Backup only what you need to backup
The backup is one of the most crucial regular steps in your schedule. It consumes time, effort, hardware and cost. The backup process must be well organized to avoid mistakes and excessive time consumption. While many people aim to categorize the backup files based on their type, it is important to keep in mind these two main factors while choosing the backup type: 1) Only backup the necessary files (such as project source files), important documentation (such as contracts), project documents and plans. Also backup the files that are hard to find again or already located on the web, such as free software, browsers, source files and so on. Minimizing the backup of these files will help in reducing the size of the output files; the backup and restore processes will also take less time. 2) Plan your backup structure carefully and how you actually want to backup your files. Actually, it is more related to your own arrangement of the files and how you arrange your projects source files. Implementing the same arrangement would prevent becoming lost in the middle of many projects and files and avoid any mistakes. Such mistakes usually happen because of the confusion between your own files arrangement and the backup arrangement.How to choose backup devices
As mentioned, backups depend on saving data in another location to be able to retrieve it if the original data is lost or corrupted. The backup process uses the available storage technologies to store the files. Throughout the history of the computer and even before it, there were many forms to save data from punched cards to magnetic tapes, and finally hard disks and Blu-ray technology. Storage media is constantly improving by increasing in capacity and applying new technologies as well as further developing existing technology. While the devices change based on technology, choosing a suitable storage device for the backup depends on some important points when choosing the device:The storage capacity
The storage devices vary in capacity and their ability to save large files; you should put this into consideration when choosing the best storage media if you plan to create frequent backups.The price
The cost of the backup device is one of the most important issues that you should consider as you may need to use more than one device based on their storage capacity. If you are using online backup tools, you should consider the cost of the storage space and if you will eventually need extra space on the server to host your files.The ability to extend or rewrite
Rewritable devices are more flexible and allow adding more content each time you create the backup instead of using a new device each time. Also, the extended devices can help you keep all the files in one place instead of spreading it across multiple devices.Durability
Durability is essential in backup media as its sole purpose is to store files in case of an emergency. When determining suitability, the question is how easy will the data corrupt under normal circumstances?Portability
If your business requires a lot of moving, then you need to think about the portability of the device as well as it’s durability throughout.The transfer speed
When you transfer the backup data from the computer to the device, you need to have a fast transfer media to achieve this in the least time-consuming manner; therefore is the speed of transferring data another factor to put into consideration when buying the backup hardware. Transfer speed is one of the most important factors in online backup storage. Although it is mainly dependent upon your internet connection speed, the server transfer speed varies throughout the day.Backup devices
Storage devices vary based on the above factors and are updated frequently with new technologies and storage capabilities. The following briefly summarize storage media based on their type.Optical discs
This includes CDs, DVDs and Blu-ray discs; they vary on their storage size and their rewrite-ability as following:Compact Discs (CDs):
CDs are the lowest sized optical storage devices; they come in CD-R, or CD-RW which allow rewriting content on the CD many times. They can save up to 700 MB; more information can be found here. Advantages: CDs are cheap, portable and compatible with both DVD-ROM and CD-ROM drives. Disadvantages: Low capacity, can easily be damaged or scratched and are known as one of many non-secured media.Digital Versatile Discs (DVDs):
This is the next stage in developing optical discs and has greater storage space compared with CDs. DVDs can store up to 4.7 GB. DVDs are commonly used these days when compared with CDs because of their storage ability which was the main problem with CDs. Advantages: DVDs share the advantages of CDs but also have the ability to store larger content up to 4.7 GB. Disadvantages: The disadvantages of DVDs are the same as CDs and also they aren’t compatible with older disc drives.Blu-ray discs
Blu-ray discs are the latest optical technology that supersede DVDs. They also allow storing massive amounts of data that can reach 25 GB for single layer discs and 50GB for double layer discs. Advantages: Blu-ray discs have similar plus points just like other optical discs, in addition to the ability to store large amounts of data. This is why it is mainly used for PlayStation video games and to store HD video. Disadvantages: Its price is still quite high, compared to other optical discs and its storage capacity. Also, blu-ray discs drives are not commonly used compared to other discs drives.Hard Disks
Hard disks have been developed a lot and have massive storage capabilities. Hard disks let you store large data that can reach TBs. It is the most commonly used and largest storage media. Hard disks implement different interfaces to transfer data such as using ATA, SCSI, SATA, USB, FireWire and eSATA. Advantages: Hard disks have a large storage size that increases dramatically and its price is consistently falling. Also, it ensures fast data transfer along with the easy ability to rewrite and update content. Unlike optical discs, hard disks can be secured and allow adding passwords to the content. Disadvantages: Hard disks are easily damaged, especially when in transit. They should be treated with great care and not moved excessively.USB Flash Drives
USB memory sticks are an easy, portable substitution for hard disks that can be easily carried and transported with far higher durability than normal disks. Their storage capacities vary and expand as technology itself develops. Advantages: USB Flash drives are the most suitable portable devices as they are easy to transport and durable against shocks compared with other storage devices. Also, it can be easily attached to a computer and function in a similar way to Hard Drives. Disadvantages: Due to its light weight and small size, USB Flash drives can be easily lost. Also, their prices are higher than hard disks per gigabyte.Remote backup
With the increasing speed of the internet and the ability to transfer large amounts of data in a short space of time, remote backup is becoming one of the most efficient solutions to store backups, especially in large disasters that can happen in the workplace or company location. The remote backup saves the data using an encrypted format to remote storage servers where the data can be removed or downloaded when required. Remote backups, either through the internet or network can be a good solution to store data in a secure place and retrieve the data without the need to transport it or move it as is the case when using the other storage devices above. Advantages: It provides better secured data storage as the data is saved in a different location from the source data. Also, its storage avoids being transported which reduces the chance of the files corruption. Remote backup methods are more extendable than other methods as the data is stored in locations created especially for this reason and you can download the data or restore it from anyplace. On the other hand, the saved data is secured by a secret key that prevents viewing the data without it. Disadvantages: The biggest disadvantage of remote backup is the price; it is expensive to buy storage space compared with other methods. Also, it requires a fast internet connection to work properly and not to cause any delay. Generally, choosing the backup device depends on your needs and business requirements; you have to select the best method that fits with the stored data and how it should be handled.Backup applications
Choosing the right backup application or tool is the next step to complete your backup system and arrange the backup process. In this stage, we will look at the backup applications we can use to perform the backup. These applications can be freeware, shareware or paid applications depending on its policy which can be updated. As mentioned above, the backup can be done through offline backup storage, such as optical discs and hard disks, as well as online backups through the network or the internet. Therefore, backup applications can be categorized as either offline tools and online tools. While some of the offline tools may allow you to upload the backup files to remote servers, they are mainly designed to do the backup offline on the local machine and then give you the ability to upload it. Also, it does not provide online storage similar to the full online backup tools that we will see later.Offline backup tools
These tools can be used to backup files and store them on storage devices that were discussed earlier. The following list includes some of the commonly used backup tools:Cobian Backup 10 (Freeware - Win)
 It is a multi-threaded application that you can use to backup files and folders from the local machine and store them in another destination or upload it to an FTP account. Cobian backup can save the stored files in both a compressed and non-compressed format.
It is a multi-threaded application that you can use to backup files and folders from the local machine and store them in another destination or upload it to an FTP account. Cobian backup can save the stored files in both a compressed and non-compressed format.
DeltaCopy (Freeware - Win)
 DeltaCopy is an open source backup tool that is based on the incremental backup method to save the files. It reduces the backup and restores time. DeltaCopy can run based on a scheduled time with one click to restore the saved files.
DeltaCopy is an open source backup tool that is based on the incremental backup method to save the files. It reduces the backup and restores time. DeltaCopy can run based on a scheduled time with one click to restore the saved files.
AceBackup (Freeware - Win)
 With Acebackup, you can store the backed up files on different storage media as well as the ability to upload the backup files to a remote FTP account. Also, it supports different compression and encryption methods for the files. Similar to other backup tools, it can be scheduled to do the backup process in specified times.
With Acebackup, you can store the backed up files on different storage media as well as the ability to upload the backup files to a remote FTP account. Also, it supports different compression and encryption methods for the files. Similar to other backup tools, it can be scheduled to do the backup process in specified times.
SyncToy (Freeware - Win)
 SyncToy is basically a synchronization application between files and folders and it can create backup copies of these files and folders. SyncToy's new version includes better error handling than the previous one. In addition to the new features, it also includes the ability to filter files based on one or more attributes and manage folders through the command line interface.
SyncToy is basically a synchronization application between files and folders and it can create backup copies of these files and folders. SyncToy's new version includes better error handling than the previous one. In addition to the new features, it also includes the ability to filter files based on one or more attributes and manage folders through the command line interface.
Personal Backup (Freeware - Win)
 Personal-backup saves the backup files to both local and remote storage locations with the ability to include or exclude folders and files based on manual selection or using filters. It maintains the original files architecture and compresses the files as Gzip or Zip.
Personal-backup saves the backup files to both local and remote storage locations with the ability to include or exclude folders and files based on manual selection or using filters. It maintains the original files architecture and compresses the files as Gzip or Zip.
Allway Sync (Freeware - Win)
 Allway Sync is a free, personal backup tool that allows you to backup files and folders as well as synchronizes them with an easy to use interface. It can also backup files on local devices or through the network.
Allway Sync is a free, personal backup tool that allows you to backup files and folders as well as synchronizes them with an easy to use interface. It can also backup files on local devices or through the network.
Hinxsoft (Freeware - Win)
 Hinxsoft backup tool allows automatic backup of files and folders with multi-language support. This application is written in Java and comes with a simple interface. The backed up files can be saved on local devices or FTP using SSL and SFTP.
Hinxsoft backup tool allows automatic backup of files and folders with multi-language support. This application is written in Java and comes with a simple interface. The backed up files can be saved on local devices or FTP using SSL and SFTP.
Comodo BackUp (Freeware - Win)
 Comodo is a free backup and recovery application that includes some useful features in addition to the ordinary backup features such as quickly restoring data, multiple compression options, email notification with the backup status and securing features through password and data encryption.
Comodo is a free backup and recovery application that includes some useful features in addition to the ordinary backup features such as quickly restoring data, multiple compression options, email notification with the backup status and securing features through password and data encryption.
SyncBackSE (Commercial with 30 days trial version- Win)
 SyncBackupSE saves files with ‘fast backup’ and ‘smart synchronization’. It keeps the previous backup versions and creates a new version with every new backup.
SyncBackupSE saves files with ‘fast backup’ and ‘smart synchronization’. It keeps the previous backup versions and creates a new version with every new backup.
Acronis Backup and Security (Commercial with free trial - Win)
 Acronis is another commercial backup tool; it lets you schedule the backup process and create encrypted backup content. It also provides a secure backup for files and gives you the ability to adjust your system resources such as the CPU and bandwidth allocated to the Acronis backup process. Acronis allows you to recover files from different points in the backup version as well, so you can revert to the points where the data isn’t corrupted, and it provides protection to multiple computers at the same time.
Acronis is another commercial backup tool; it lets you schedule the backup process and create encrypted backup content. It also provides a secure backup for files and gives you the ability to adjust your system resources such as the CPU and bandwidth allocated to the Acronis backup process. Acronis allows you to recover files from different points in the backup version as well, so you can revert to the points where the data isn’t corrupted, and it provides protection to multiple computers at the same time.
ChronoSync (Commercial with demo version available– Mac)
 ChronoSync is a Mac backup application that provides a tool to synchronize files, backup files and create bootable backups where you can boot to your backup files and run your Mac from the backup. Similar to the rest of the backup tools, ChronoSync provides a scheduled sync of your files.
ChronoSync is a Mac backup application that provides a tool to synchronize files, backup files and create bootable backups where you can boot to your backup files and run your Mac from the backup. Similar to the rest of the backup tools, ChronoSync provides a scheduled sync of your files.
Tri-Backup 5 (Commercial – Mac)
 It is an easy to use backup utility for your Mac files and folders as it provides the ability to create a bootable copy of the hard disk, compression and encryption for the files, automatic upgrades and the ability to work in the background while your applications are running.
It is an easy to use backup utility for your Mac files and folders as it provides the ability to create a bootable copy of the hard disk, compression and encryption for the files, automatic upgrades and the ability to work in the background while your applications are running.
SuperDuper (Commercial with free limited version – Mac)
 This utility includes common backup tasks along with simple and clear language. Also, it is working perfect with both Intel and Power PC Macs.
This utility includes common backup tasks along with simple and clear language. Also, it is working perfect with both Intel and Power PC Macs.
Carbon Copy Cloner (Freeware – Mac)
 It is a free backup application that lets you backup, synchronize and clone your data using the incremental backup to create fast backups since it only saves the changes that happened based on the previous version of the backup data. Carbon Copy archives the items that have been deleted from the source and backs up the files to the hard drive or a disk image.
It is a free backup application that lets you backup, synchronize and clone your data using the incremental backup to create fast backups since it only saves the changes that happened based on the previous version of the backup data. Carbon Copy archives the items that have been deleted from the source and backs up the files to the hard drive or a disk image.
Online backup
Online backup tools depend on storing files as encrypted data on the server where you register a specific space and pay for it on a monthly or annually basis. The following online backup applications provide examples of online tools and how they work.Acronis Online Backup (Commercial with free trial- Win)
 Acronis provides an online backup tool that lets you backup data up to 250GB with full security and protection. Also you can use it to store your data and download it from anywhere without the need to transport your data everywhere you go. Acronis Online Backup subscription can be either on a monthly or a yearly plan. You can use the account to backup one or more PCs or laptops.
Acronis provides an online backup tool that lets you backup data up to 250GB with full security and protection. Also you can use it to store your data and download it from anywhere without the need to transport your data everywhere you go. Acronis Online Backup subscription can be either on a monthly or a yearly plan. You can use the account to backup one or more PCs or laptops.
Carbonite (Commercial with free trial - Win)
 Carbonite provides different subscription plans to join their backup service which include one, two or three year periods. Carbonite provides secure online storage for the backup by using up-to-date encryption.
Carbonite provides different subscription plans to join their backup service which include one, two or three year periods. Carbonite provides secure online storage for the backup by using up-to-date encryption.
Mozy (Commercial – Win and Mac)
 Mozy is one of the most comprehensive online backup utilities that provides encryption for the backed up data as well as automatic detection of changes in the files and backing up. On the other hand, it supports the backup of open and locked files and an automatic, scheduled backup. Mozy is using the incremental backup method to store the files and lets you decide the bandwidth you would like to dedicate for the backup process. Mozy provides a free account that includes 2 GB of free backup space to trial without the need to add any payment information.
Mozy is one of the most comprehensive online backup utilities that provides encryption for the backed up data as well as automatic detection of changes in the files and backing up. On the other hand, it supports the backup of open and locked files and an automatic, scheduled backup. Mozy is using the incremental backup method to store the files and lets you decide the bandwidth you would like to dedicate for the backup process. Mozy provides a free account that includes 2 GB of free backup space to trial without the need to add any payment information.
IDrive (Commercial – Win and Mac)
 This utility is using the incremental method and saves only the changes that occur in the files; this saves a lot of space and increases the backup speed and can be helpful in the online backup process. IDrive provides other features such as the option to automate the backup of common files such as photos, documents and videos. IDrive can detect changes in files and back it up every 10 minutes as well as apply encryption to it. Also, it can backup open and locked files, external hard drives and restore data from anywhere using the fast search feature. You can try IDrive through the free account which provides 2 GB free storage to store files and backup data.
This utility is using the incremental method and saves only the changes that occur in the files; this saves a lot of space and increases the backup speed and can be helpful in the online backup process. IDrive provides other features such as the option to automate the backup of common files such as photos, documents and videos. IDrive can detect changes in files and back it up every 10 minutes as well as apply encryption to it. Also, it can backup open and locked files, external hard drives and restore data from anywhere using the fast search feature. You can try IDrive through the free account which provides 2 GB free storage to store files and backup data.
Dropbox (Commercial – Win and Mac)
 Dropbox includes file sync, file sharing and online backup for your files. It enables automatic updates for the files, even if you are working offline, as once you connect your computer to the internet, Dropbox starts to synchronize the files and makes sure you have the latest updates on the server. Through the paid account, you can undo file changes to an unlimited number of versions. You can try Dropbox through their free account with 2 GB of space and undo for up to 30 days.
Dropbox includes file sync, file sharing and online backup for your files. It enables automatic updates for the files, even if you are working offline, as once you connect your computer to the internet, Dropbox starts to synchronize the files and makes sure you have the latest updates on the server. Through the paid account, you can undo file changes to an unlimited number of versions. You can try Dropbox through their free account with 2 GB of space and undo for up to 30 days.

That’s exactly what I was looking for: an updated list for backup utilities. Kudos!
I would have thought Time Machine on Mac would have merited a mention for its simplicity and being free!
Yeah… Agree with Derek. Time Machine is the default backup method for the majority of Mac users due to the high level of integration with OS X.
I didn’t believe it was actually not mentioned at first. I thought, “Well, he probably said it in passing because of the fact that it is so ubiquitous.” But there isn’t a single mention at all.
Thanks for the massive list of backup products, exactly what I was looking for. Thanks again!
I had the same thought. I use Time Machine every day (well, every hour, as it were). I love how it does it all for me. I don’t have to give it a second thought. I have so much more peace of mind now.
Maybe someone could suggest some program to backup files from ftp to hdd?
I have signed my company up to the 50GB Dropbox for a measly $99 a year, and then use it as the sole place for storing all our business’ files. Think of it as the company’s “My Documents” folder.
The benefit of this is that whenever a file is saved, it is instantly backed-up online and off-site – no having to ‘think’ about backing it up, or remembering to leave a computer running overnight to perform a system backup to disc. Also, any time I sync another computer to the Dropbox account (i.e. my laptop at home), that there becomes and off-site backup in itself.
I therefore never really have to think about making backups at all. Naturally I do make use of an Apple Time Capsule and OSX Time Machine to automatically make full machine backups every hour, day, week and month to an external HDD – but that is just a precaution to enable me to reboot my entire system should it be required. But in the case of my most important files, I’m safe in the knowledge that my files are backed up in multiple locations both on and offline, and are never out of date.
Oh… and did I mention Dropbox’s built in versioning system to restore previous copies of files – saved my a** a couple of times! :-)
I have also used DriveImage XML for moving a hard drive to another, worked perfectly.
Al
Just to add to this interesting list a simple tool for Windows: Create Synchronicity (http://synchronicity.sourceforge.net/) that I like right now.
The backup methods and devices here is very useful information. Really very helpful.
Thanks for sharing such a nice article.
Backup utiliies are most important and plays crucial role to keep you out of any data loss conditions. But people messed up with daily routine of taking backup and in the end they found themselves with all their data lost forever.
There is only one way to keep out even if you don’t have any backup, Using data recovery software and services. But it could be little bit costly then taking backup.
Thanks for such a nice piece of article.